Are you fed up with unwanted guests in your bed? No, we're not talking about your partner stealing the duvet or your pet wanting to take a nap. We're talking about those little crawlers that call the bed their home: bed bugs and bed bugs.
Yes, they are not the most charming bed partners, but it is important to know the difference between these two creatures. Because believe it or not, there are a number of essential differences between bed bugs, head lice, carpet beetles and bed bugs. So before you run to bed in fear of a lice invasion, let's take a look at what exactly sets these critters apart. Don't be fooled by their small size, because these lice have more than enough tricks up their sleeves.
What are bedbugs?
Bed bugs, also known as Cimex hemipterus, are similar to bed bugs. They also belong to the same family, but there are some differences between the two species. Bed bugs are known for their preference for tropical climates and can be found in areas with high humidity. They also feed on blood, often from humans, and hide in cracks and crevices.
What are bed bugs?
Bed bugs, also called Cimex lectularius, belong to the Cimicidae family. They are small, oval insects that are mainly active at night. These leeches feed on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Bed bugs have flat bodies, which makes them easy to hide in cracks and crevices, such as in mattresses, furniture and behind baseboards.
What are similarities between bed bugs and bed bugs
Although there are some differences, bed bugs and bed bugs also share many similarities:
- Feeding: Both insects feed on the blood of humans or other hosts. They bite their victims at night, leaving nasty and itchy bites.
- Hiding: Both bed bugs and bed bugs are excellent hiders and can hide in a variety of environments, such as mattresses, bedding, furniture, carpets and clothing. This makes it difficult to detect and eradicate them.
- Disease transmission: Although both insects are not known for spreading serious diseases, their bites can lead to rashes, allergic reactions and even infections due to scratching.
What is the difference between bedbugs and bedbugs?
In the world of pest control, the terms bed bugs and bed bugs are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion. Although both pests can cause discomfort and nuisance, there are important differences between the two. In this article, we delve deeper into the characteristics, life cycles, and control methods of bed bugs and bed bugs to provide clarity and effective solutions.
What are the characteristics of bedbugs?
Bed bugs, also known as head lice, mainly live on the scalp of people. They are very small, about 2 to 3 millimeters long, and have a reddish brown color. Bed bugs feed on human blood, causing itchy bumps and irritation on the scalp. Their presence can usually be recognized by the fine, white eggs (nits) they leave behind on hair strands close to the scalp.
Transmission and Prevention: Bed bugs spread through direct contact with the hair of an infected person or by sharing personal items such as combs, hats or pillowcases. Prevention focuses primarily on personal hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items.
What are the characteristics of Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs are small, oval, brownish insects that live on the blood of people and animals. Adult specimens can grow up to 5 millimeters in length. They hide in dark, hidden places such as mattress seams, bed frames, and behind wallpaper during the day, and emerge at night to feed.
Transmission and Prevention: Bed bugs spread by hitching a ride on clothing, luggage, furniture, and other objects that are moved from one place to another. Preventive measures include regular inspection of sleeping areas, using protective covers for mattresses, and avoiding purchasing second-hand furniture without thoroughly inspecting it first.
The Life Cycle and Reproduction of Bed Lice and Bed Bugs
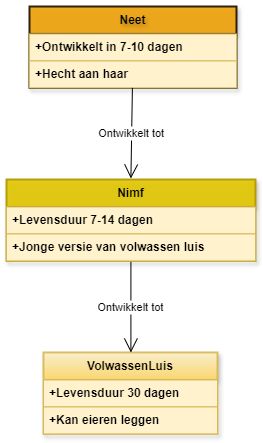
Bed bugs have a life cycle consisting of three stages: egg (nit), nymph, and adult louse. The complete cycle from egg to adult louse takes about 3-4 weeks. Female lice can lay up to ten eggs per day, which allows for rapid multiplication.
Bed bugs also go through three life stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Their life cycle from egg to adult insect can vary from 5 weeks to several months depending on environmental conditions. Female bed bugs lay hundreds of eggs in their lifetime, allowing for rapid spread and colonization of new areas.
Although they look similar as just mentioned, there are also some important differences between bed bugs and bed bugs:
- Appearance: Bed bugs have a brownish-red color with a flat, oval-shaped body. Bed bugs, on the other hand, have a darker, more elongated body.
- Preferred Habitat: Bed bugs prefer temperate climates and can be found in both warmer and colder areas. However, bed bugs thrive better in tropical environments with high humidity.
- Reproduction Rate: Bed bugs have a reputation for reproducing faster than bed bugs. A single female can lay up to 500 eggs over her lifetime, while bedbugs lay fewer eggs.
- Behavior: Bed bugs tend to be slightly more aggressive than bed bugs and are more capable of re-bleeding. Bed bugs, on the other hand, may not feed frequently because they can survive for months without food in certain conditions.
Methods to combat bed bugs, bed bugs and carpet beetlesIn the fight against uninvited guests in our homes, such as bedbugs, bedbugs, and not to forget, carpet beetles, we face several challenges. Carpet beetles, which are sometimes confused with bedbugs and bedbugs, also pose a significant problem as pests. Each of these pests requires a unique approach for effective control. In the following sections, we'll explore the recommended control methods for each of these pests and summarize the information in an easy-to-read table so you can get a clear idea of how to best tackle each type of pest.
The best methods to combat bedbugs and bedbugs:
Bed bugs and bed bugs require a similar approach to control, including:
- Dimeticon lotion for the treatment of head lice, reducing the risk of bed lice.
- Regularly wash bedding at a minimum of 60°C to kill all lice and nits.
- Call in professional help for thorough control with steam & heat.
-
Tea tree oil and vacuuming as natural and preventive measures.
The treatment of bedbugs
Treating head lice with dimethicone lotion An effective way to tackle head lice is to use dimethicone lotion, such as that available at Luizenweg.nl . This specific treatment kills head lice by suffocating them, without the use of pesticides, preventing resistance. When head lice are treated and killed effectively, you also prevent the risk of so-called bed lice. These are not separate lice, but head lice that can temporarily survive outside the scalp, such as on bedding, when they fall from the head.
It is important to know that although the term 'bed bugs' is sometimes confused with bed bugs, they are directly related to the presence of head lice. By successfully treating head lice with dimethicone lotion from Luizenweg.nl, you reduce the risk of 'bed lice'. In addition, to ensure complete elimination of lice, it is advisable to wash the bedding. This will help remove any remaining lice or nits that may have landed on the bedding. A wash at a minimum of 60°C is recommended to ensure that all lice and nits are effectively killed.
The treatment of bed bugs
- Bed bug treatment involves several methods that can be effective in eradicating these unwanted guests from your home. Here are some key points:
- Tea tree oil : A natural method of treating bed bugs is cleaning your home with tea tree oil . This strong oil is unpleasant for bed bugs and can help get rid of them.
- Professional help : For thorough treatment of bed bugs, it is often necessary to call in a professional pest controller who specializes in the use of steam & heat for a non-toxic treatment.
- High temperature washing : Regularly washing bedding, clothing and other fabrics at high temperatures can effectively kill bed bugs and is an important part of bed bug treatment .
- Vacuuming : Regular and thorough vacuuming, especially around the bed and sleeping area, can help reduce bed bug populations as part of bed bug treatment .
It is important to remember that bed bugs are persistent and treatment for bed bugs often requires multiple methods and repeated efforts to completely eradicate them.
The treatment of carpet beetles
- Thorough vacuuming : Regular vacuuming, especially around and under furniture, can help remove carpet beetle larvae and eggs.
- High temperature washing : As with bed bugs, washing infested fabrics at a high temperature can help kill carpet beetles.
- Insecticides : The use of insecticides specifically targeted at carpet beetles can be effective if applied according to the instructions on the product.
Pest treatment comparison table
Pest Heat treatment Cold treatment Chemical treatment Other methods Bed bugs Yes (60°C+) Yes (-14°C) Yes Wash at high temperature Carpet beetles Yes (effective) N/A Yes Vacuum thoroughly Bed Lice (Head Lice on Bedding) Yes (wash at 60°C+) N/A Specific lice treatments for textiles Regular washing of bed linen; Using lice-killing sprays for bedding Note: For effective control of head lice itself, treatments such as using dimethicone lotion on the head, combing with a fine-toothed comb , and following specific instructions for using lice products are essential. This table focuses on minimizing their survival and spread through bedding and similar surfaces.
Final conclusion:
The Fight Against Bedbugs, Bed Bugs, and Carpet Beetles.
When confronted with bedbugs, bedbugs and carpet beetles, thorough knowledge and a proactive approach appear to be essential for effective prevention and control. Bedbugs and bugs share a tendency to feed on blood, while carpet beetles damage textiles, underscoring how diverse the strategies must be to tackle each of these pests.
The use of dimethicone lotion is highly recommended for effectively treating head lice , with preventive measures such as regular washing of bedding at high temperatures being crucial to prevent bed lice. This approach not only helps control lice but also helps reduce the risk of bed bugs.
Regular inspection and cleaning of potential hiding and feeding places is important for carpet beetles. Minimizing their habitat through good hygiene practices can help control their population.
In summary , the key to success in controlling bed bugs, bed bugs and carpet beetles lies in the combination of targeted treatments and preventive measures. By keeping the environment clean and inspected, and by acting quickly and effectively at the first signs of an infestation, households can protect themselves from the inconveniences caused by these pests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I identify bedbugs or bedbugs?
You can identify bedbugs and bedbugs by looking at their physical characteristics. Bed bugs have a flat, oval-shaped body with a brownish-red color, while bedbugs are darker and more elongated.
2. Are bedbugs and bedbugs dangerous to my health?
Although bedbugs and bedbugs do not spread serious diseases, their bites can lead to itching, rashes and allergic reactions. Excessive scratching can also lead to infections.
3. How can I prevent a bedbug or bedbug infection?
To prevent an infestation of bedbugs or bedbugs, it is important to regularly clean your bedding, clothes and carpets. Also make sure you don't bring in second-hand furniture or mattresses without thoroughly inspecting them.


